Tags
Abdication, Crown Prince Frederik of Denmark, Crown Princess Mary of Denmark, Dagmar of Demark, Empress Alexandra Feodorovna of Russia, Empress Maria Feodorovna of Russia, Grand Duchess Olga Alexandrovna of Russia, Grand Duke Michael of Russia, Grigori Rasputin, King Christian X of Denmark, Nicholas II of Russia, Peter and Paul Cathedral, Prince Michael of Kent, Queen Alexandra of the United Kingdom, Queen Margrethe II of Denmark., Russian Revolution, St. Petersburg
In Kiev, Maria engaged in the Red Cross and hospital work, and in September, the 50th anniversary of her arrival in Russia was celebrated with great festivities, during which she was visited by her son, Nicholas II, who came without his wife. Empress Alexandra wrote to the Emperor: “When you see Motherdear, you must rather sharply tell her how pained you are, that she listens to slander and does not stop it, as it makes mischief and others would be delighted, I am sure, to put her against me…” Maria did ask Nicholas II to remove both Rasputin and Alexandra from all political influence, but shortly after, Nicholas and Alexandra broke all contact with the Emperor’s family.
When Rasputin was murdered, part of the Imperial relatives asked Maria to return to the capital and use the moment to replace Alexandra as the Emperor’s political adviser. Maria refused, but she did admit that Alexandra should be removed from influence over state affairs: “Alexandra Feodorovna must be banished. Don’t know how but it must be done. Otherwise she might go completely mad. Let her enter a convent or just disappear”.

Revolution and exile
Revolution came to Russia in 1917, first with the February Revolution, then with Nicholas II’s abdication on March 15. After travelling from Kiev to meet with her deposed son, Nicholas II, in Mogilev, Maria returned to the city, where she quickly realised how Kiev had changed and that her presence was no longer wanted. She was persuaded by her family there to travel to the Crimea by train with a group of other refugee Romanovs.
After a time living in one of the imperial residences in the Crimea, she received reports that her both of her sons, (Emperor Nicholas II and his brother Grand Duke Michael) her daughter-in-law and her grandchildren had been murdered. However, she publicly rejected the report as a rumour. On the day after the murder of the Emperor’s family, Maria received a messenger from Nicky, “a touching man” who told of how difficult life was for her son’s family in Yekaterinburg. “And nobody can help or liberate them – only God! My Lord save my poor, unlucky Nicky, help him in his hard ordeals!”
In her diary she comforted herself: “I am sure they all got out of Russia and now the Bolsheviks are trying to hide the truth.” She firmly held on to this conviction until her death. The truth was too painful for her to admit publicly. Her letters to her son and his family have since almost all been lost; but in one that survives, she wrote to Nicholas: “You know that my thoughts and prayers never leave you. I think of you day and night and sometimes feel so sick at heart that I believe I cannot bear it any longer. But God is merciful. He will give us strength for this terrible ordeal.”
Maria’s daughter Olga Alexandrovna commented further on the matter, “Yet I am sure that deep in her heart my mother had steeled herself to accept the truth some years before her death.”

Despite the overthrow of the monarchy in 1917, the former Empress Dowager Maria at first refused to leave Russia. Only in 1919, at the urging of her sister, Dowager Queen Alexandra, did she begrudgingly depart, fleeing Crimea over the Black Sea to London. King George V sent the warship HMS Marlborough to retrieve his aunt. The party of 17 Romanovs included her daughter the Grand Duchess Xenia and five of Xenia’s sons plus six dogs and a canary.
After a brief stay in the British base in Malta, they travelled to England on the British ship the Lord Nelson, and she stayed with her sister, Alexandra. Although Queen Alexandra never treated her sister badly and they spent time together at Marlborough House in London and at Sandringham House in Norfolk, Maria, as a deposed Dowager Empress , felt that she was now “number two,” in contrast to her sister, a popular queen dowager, and she eventually returned to her native Denmark. After living briefly with her nephew, King Christian X, in a wing of the Amalienborg Palace, she chose her holiday villa Hvidøre near Copenhagen as her new permanent home.
There were many Russian émigrées in Copenhagen who continued to regard her as the Empress and often asked her for help. The All-Russian Monarchical Assembly held in 1921 offered her the locum tenens of the Russian throne but she declined with the evasive answer “Nobody saw Nicky killed” and therefore there was a chance her son was still alive. She rendered financial support to Nikolai Sokolov, who studied the circumstances of the death of the Emperor’s family, but they never met. The Grand Duchess Olga sent a telegram to Paris cancelling an appointment because it would have been too difficult for the old and sick woman to hear the terrible story of murder of her son and his family.

Death and burial
In November 1925, Maria’s favourite sister, Queen Alexandra, died. That was the last loss that she could bear. “She was ready to meet her Creator,” wrote her son-in-law, Grand Duke Alexander Mikhailovich, about Maria’s last years. On October 13, 1928 at Hvidøre near Copenhagen, in a house she had once shared with her sister Queen Alexandra, Maria died at the age of 80, having outlived four of her six children. Following services in Copenhagen’s Russian Orthodox Alexander Nevsky Church, the Empress was interred at Roskilde Cathedral.
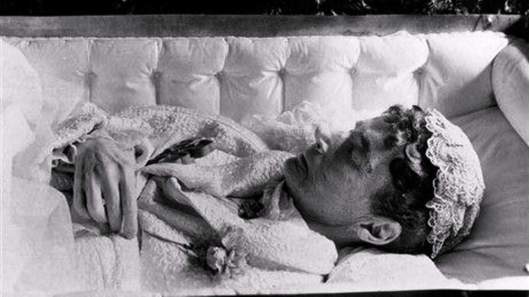
In 2005, Queen Margrethe II of Denmark and President Vladimir Putin of Russia and their respective governments agreed that the Empress’s remains should be returned to St. Petersburg in accordance with her wish to be interred next to her husband. A number of ceremonies took place from September 23 to 28, 2006.
The funeral service, attended by high dignitaries, including the Crown Prince Frederik and Crown Princess Mary of Denmark and Prince and Princess Michael of Kent, did not pass without some turbulence. The crowd around the coffin was so great that a young Danish diplomat fell into the grave before the coffin was interred.

The reburial of Empress Maria Feodorovna of Russia in St. Petersburg
On September 26th, 2006, a statue of Maria Feodorovna was unveiled near her favourite Cottage Palace in Peterhof. Following a service at Saint Isaac’s Cathedral, she was interred next to her husband Emperor Alexander III in the Peter and Paul Cathedral on September 28, 2006, 140 years after her first arrival in Russia and almost 78 years after her death.











